Achalasia is a rare swallowing disorder that affects how food and liquid move from your esophagus into your stomach. When left untreated, symptoms often worsen over time and interfere with nutrition, comfort, and quality of life. Understanding achalasia treatment options helps you make informed decisions and seek care early.
This article explains achalasia treatment in detail. You will learn about medical and procedural options, how treatments work, what to expect long term, and how to manage daily life with achalasia.
What Is Achalasia and Why Treatment Matters
Achalasia occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter fails to relax properly. The esophagus also loses normal muscle movement.
Without effective achalasia treatment, food builds up in the esophagus. This can cause pain, regurgitation, weight loss, and aspiration.
Early treatment improves swallowing and prevents complications.
Goals of Achalasia Treatment
The primary goal of achalasia treatment is symptom relief.
Treatment focuses on reducing pressure at the lower esophageal sphincter.
While achalasia cannot be cured, symptoms can be well controlled long term.
How Achalasia Is Diagnosed Before Treatment
Proper diagnosis ensures the right achalasia treatment plan.
Tests often include esophageal manometry, barium swallow studies, and endoscopy.
These tests assess muscle function, structure, and rule out other causes.
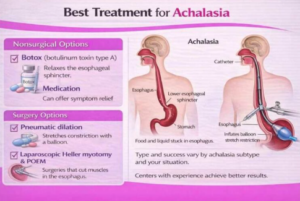
Non-Surgical Achalasia Treatment Options
Medications for Achalasia
Medications are usually reserved for mild symptoms or patients unable to undergo procedures.
Nitrates and calcium channel blockers help relax the lower esophageal sphincter.
Medication-based achalasia treatment provides limited and temporary relief.
Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injection
Botox injections weaken the sphincter muscle.
This achalasia treatment is performed during endoscopy and does not require surgery.
Relief is often short term and may require repeat injections.
Endoscopic Achalasia Treatment Procedures
Pneumatic Balloon Dilation
Balloon dilation stretches the lower esophageal sphincter.
It is one of the most common achalasia treatment options.
Symptoms often improve significantly after one or more sessions.
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)
POEM is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure.
It cuts the muscle fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter internally.
POEM is an effective achalasia treatment for many subtypes.
Surgical Achalasia Treatment Options
Heller Myotomy Surgery
Heller myotomy involves cutting the sphincter muscle surgically.
It is often combined with anti-reflux surgery.
This achalasia treatment has strong long-term success rates.
When Surgery Is Recommended
Surgery is considered for younger patients or severe disease.
It is also used when other achalasia treatment options fail.
Comparing Achalasia Treatment Options
Each achalasia treatment has benefits and limitations.
Balloon dilation is effective but may need repeat procedures.
POEM and surgery offer longer relief but carry reflux risk.
Treatment choice depends on age, achalasia type, and overall health.
Risks and Side Effects of Achalasia Treatment
Most achalasia treatment options are safe when performed by specialists.
Potential risks include reflux, perforation, or infection.
Long-term acid reflux is a common concern after muscle-relaxing treatments.
Life After Achalasia Treatment
Recovery Expectations
Recovery time varies by treatment type.
Endoscopic treatments usually allow faster return to normal activities.
Surgery may require a longer recovery period.
Diet After Treatment
You may need a soft or liquid diet initially.
Gradual food progression improves comfort and swallowing confidence.
Eating slowly and chewing well remains important.
Long-Term Management and Follow-Up
Achalasia requires lifelong monitoring.
Even after successful achalasia treatment, symptoms may recur.
Regular follow-ups help detect reflux or esophageal changes early.
Lifestyle Adjustments That Support Treatment
Sleeping with your head elevated can reduce regurgitation.
Avoid eating close to bedtime.
Smaller, frequent meals improve swallowing comfort.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with achalasia can be frustrating.
Anxiety around eating is common before and after treatment.
Education and reassurance play a key role in long-term care.
When to Seek Further Medical Attention
Persistent chest pain, weight loss, or worsening swallowing should not be ignored.
These symptoms may signal treatment failure or complications.
Prompt evaluation ensures timely adjustment of achalasia treatment.
Achalasia Treatment in Special Populations
Older Adults
Less invasive achalasia treatment options are often preferred.
Botox or balloon dilation may be safer choices.
Children and Young Adults
Long-term effectiveness is a priority.
Surgical or POEM-based achalasia treatment is often recommended.
Final Thoughts on Achalasia Treatment
Choosing the right achalasia treatment is essential for restoring swallowing comfort and protecting your long-term digestive health. With proper evaluation, individualized care, and ongoing follow-up, most people achieve meaningful symptom relief and maintain a good quality of life.
Understanding your options empowers you to work confidently with your healthcare team and manage achalasia effectively over time.
FAQ: Achalasia Treatment
- Is achalasia treatment permanent?
No. Treatment controls symptoms but does not cure the condition. - Can achalasia be treated without surgery?
Yes. Medications, Botox, and balloon dilation are non-surgical options. - What is the most effective achalasia treatment?
POEM and Heller myotomy offer the longest symptom relief. - Does achalasia treatment cure swallowing problems completely?
Often yes, but some symptoms may persist mildly. - Is achalasia treatment painful?
Most procedures are done with sedation or anesthesia. - Can achalasia come back after treatment?
Yes. Symptoms may recur over time and require retreatment. - Does achalasia treatment cause acid reflux?
Yes. Reflux is a known long-term side effect. - How long does achalasia treatment last?
Relief may last years, depending on the method used. - Is diet important after achalasia treatment?
Yes. Careful eating habits support long-term success. - When should you see a specialist again?
If symptoms return or worsen, seek evaluation promptly.